Newton's Third law: The law of action / reaction forces
For every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force.
This law is frequently confused with the first law. The most important point to make here is that the two forces (action and reaction) have to be the same force. If we consider the hanging ball again:
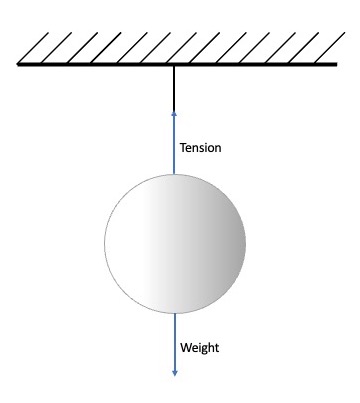
The common misconception is that if the action force is the gravitational force pulling the ball down then the reaction force is the tension force pulling the ball up. These two forces are different forces (gravitational and tension) so they cannot be an action / reaction pair.
If we want to use the hanging ball example then there are two examples of action reaction pairs. The first is if the action force is the gravitational force of the earth pulling the ball down then the reaction force is the gravitational force of the ball pulling the earth up. Note that both of these are the same type of force (gravitational) and follow the pattern:
If the action force is F A on B, then the reaction force is F B on A
Note again that both these forces are the same force.